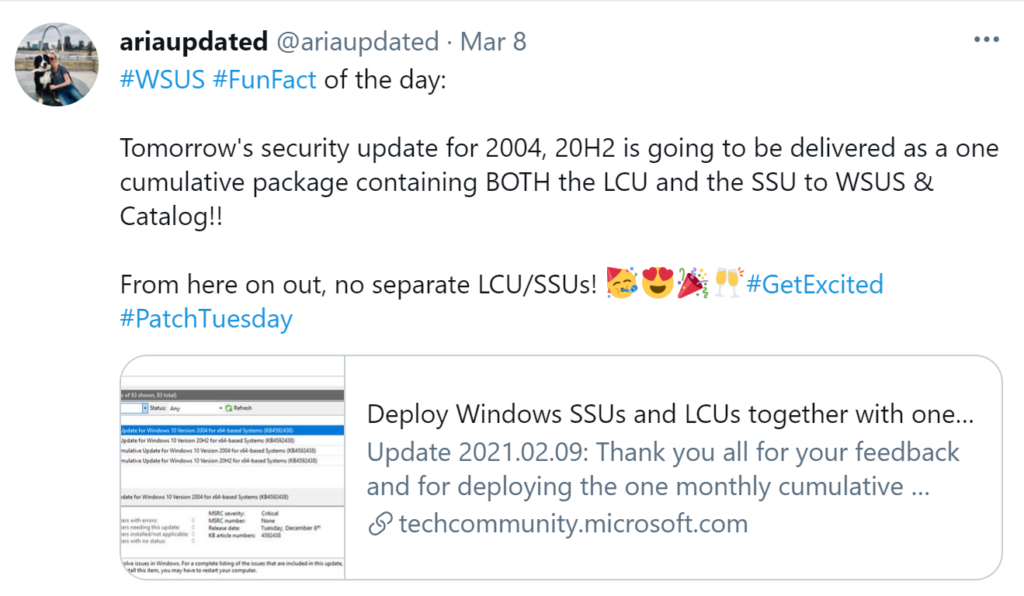
Microsoft has released fixes for 82 vulnerabilities, with 10 updates classified as Critical and 72 as Important. Here’s an updated announcement (2021-02-09) from Microsoft: Deploy Windows SSUs and LCUs together with one cumulative update –
Beginning with the February 2021 LCU, we will now publish all future cumulative updates and SSUs for Windows 10, version 2004 and above together as one cumulative monthly update to the normal release category in WSUS.
LCU = Latest Cummulative Update
SSU – Servicing Stack Update
UPDATE – 2021-03-14:
DYMO Label Printer fix for BSOD issues.

UPDATE – 2021-03-13:
Microsoft shares temporary fix for Windows 10 printing crashes
UPDATE – 2013-03-13:
Updates on Microsoft Exchange Server Vulnerabilities (CISA)
UPDATE – 2021-03-10:
Windows 10 KB5000802 (March) update is crashing PCs with BSOD
Windows 10 BSOD crashes include the both workstation and server versions running March 2021 cumulative updates:
- KB5000802: Windows 10 2004/20H2 & Windows Server 2004/20H2
- KB5000808: Windows 10 1909 & Windows Server 1909
- KB5000822: Windows 10 1809 & Windows Server 2019
- KB5000809: Windows 10 1803 & Windows Server 1803
Zero-Day Vulnerabilities Fixes:
1. Internet Explorer Memory Corruption Vulnerability (CVE-2021-26411)
2. Internet Explorer Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (CVE-2021-27085)
3. Windows Win32k Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability (CVE-2021-27077)
4. Microsoft Exchange Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (CVE-2021-27078)
Windows 10 Updates for February 2021:
- Windows 10 version 1507 — KB5000807 (OS Build 10240.18874)
- Windows 10 version 1607 — KB5000803 (OS Build 14393.4283)
- Windows 10 version 1703 — KB5000812 (OS Build 15063.2679)
(Update: 3/9/21 End of support for Windows 10, version 1703 ) - Windows 10 version 1709 — EOS
- Windows 10 version 1803 — KB5000809 (OS Build 17134.2087)
- Windows 10 version 1809 — KB5000822 (OS Build 17763.1817)
- Windows 10 version 1909 — KB5000808 (OS Build 18363.1440)
- Windows 10 version 2004 and 20H2 — KB5000802 (OS Builds 19041.867 and 19042.867) (If you are running 21H1 in the Beta Channel, see here)
Microsoft Exchange ProxyLogon attacks
Microsoft released out-of-band security updates for the ProxyLogon vulnerability that are actively being used by threat actors worldwide to compromise Microsoft Exchange servers.
These vulnerabilities are being tracked with the following CVEs:
- CVE-2021-26855 – Microsoft Exchange Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
- CVE-2021-26857 – Microsoft Exchange Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
- CVE-2021-26858 – Microsoft Exchange Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
- CVE-2021-27065 – Microsoft Exchange Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
Microsoft has released security updates for currently supported Microsoft Exchange cumulative updates and older unsupported versions.
Microsoft has released a PowerShell script called Test-ProxyLogon.ps1 that will check for indicators of compromise (IOC) in Exchange HttpProxy logs, Exchange log files, and Windows Application event logs.
March 2021 Exchange Server Security Updates for older Cumulative Updates of Exchange Server
Additional March 2021 Patching Resources:
- MSRC – March 2021 Security Updates
- Microsoft CVE Summary
- Security Update Guide – Microsoft Security Vulnerabilities
- Advisory ADV990001 for the latest service stack update (SSU)
- Adobe Security patches
- Cisco Security patches
- Apple Security patches
- Android Security Bulletin
- Oracle Security Alerts
- Google Chrome March Update
- F5 Vulnerabilities (March 2021)
- Scan Changes and certificates add security for Windows devices using WSUS for updates
- Zero Day Initiative blog
- SAP February 2021 Security Updates
- VMware View Planner update addresses remote code execution vulnerability (CVE-2021-21978)
- VMware ESXi and vCenter Server updates address multiple security vulnerabilities (CVE-2021-21972, CVE-2021-21973, CVE-2021-21974)
On March 9, 2021 (PT), Microsoft released security updates affecting the following Microsoft products:
| Product Family | Maximum Severity | Maximum Impact | Associated KB Articles and/or Support Webpages |
| Windows 10 v20H2, v2004, v1909, v1809, and v1803 | Critical | Remote Code Execution | Windows 10 v2004 and Windows 10 v20H2: 5000802 Windows 10 v1909: 5000808 Windows 10 v1809: 5000822 Windows 10 v1803: 5000809 |
| Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, and Server Core installations (2019, 2016, v20H2, v2004, and v1909) | Critical | Remote Code Execution | Windows Server 2019: 5000822 Windows Server 2016: 5000803 Windows Server v2004 and Windows Server v20H2: 5000802 Windows Server v1909: 5000808 |
| Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012 R2, and Windows Server 2012 | Critical | Remote Code Execution | Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 Monthly Rollup: 5000848 Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 Security Only: 5000853 Windows Server 2012 Monthly Rollup: 5000847 Windows Server 2012 Security Only: 5000840 |
| Internet Explorer 11 | Critical | Remote Code Execution | Internet Explorer 11 Cumulative Update: 5000800 |
| Microsoft Office-related software | Important | Remote Code Execution | 4484376, 4486673, 4493151, 4493200, 4493203, 4493214, 4493224, 4493225, 4493227, 4493228, 4493229, 4493233, 4493234, 4493239, 4504702, 4504703, 4504707 |
| Microsoft SharePoint-related software | Important | Remote Code Execution | 3101541, 4493177, 4493199, 4493230, 4493231, 4493232, 4493238 |
| Power BI Report Server | Important | Information Disclosure | 5001284, 5001285 |
| Azure-related software | Critical | Remote Code Execution | Find details on security updates for Azure-related software in the Security Update Guide: https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide |
| Microsoft Visual Studio-related software | Critical | Remote Code Execution | Find details on security updates for Visual Studio-related software at https://docs.microsoft.com/visualstudio and in the Security Update Guide: https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide |
| Windows Admin Center | Important | Security Feature Bypass | Find details on security updates for Windows Admin Center in the Security Update Guide: https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide |
| HEVC Video Extensions | Critical | Remote Code Execution | Find details on security updates for HEVC Video Extensions in the Security Update Guide: https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide |
Notes:
- The summary above is an overview of updates for the most recent versions of commonly used software.
- Updates for older versions, apps, and open source software may not be listed.
- Updates may have been added or removed from the release after this content was finalized.
- Find details for all updates in the monthly release in the Security Update Guide: https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide
- For additional details, see the release notes at: https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/releaseNote/2021-Mar
Security vulnerability overview:
Below is a summary showing the number of vulnerabilities addressed in this release, broken down by product/component and by impact.
| Vulnerability Details | RCE | EOP | ID | SFB | DOS | SPF | TMP | Publicly Disclosed | Known Exploit | Max CVSS |
| Windows 10 v20H2 & Windows Server v20H2 | 11 | 29 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 9.9 |
| Windows 10 v2004 & Windows Server v2004 | 11 | 29 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 9.9 |
| Windows 10 v1909 & Windows Server v1909 | 11 | 28 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 9.9 |
| Windows 10 v1809 & Windows Server 2019 | 10 | 26 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 9.8 |
| Windows 10 v1803 | 4 | 21 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 8.8 |
| Windows Server 2016 | 8 | 17 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 9.8 |
| Windows 8.1 & Server 2012 R2 | 8 | 12 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 9.8 |
| Windows Server 2012 | 8 | 12 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 9.8 |
| Internet Explorer 11 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 8.8 |
| Microsoft Office-related software | 7 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.8 |
| Microsoft SharePoint-related software | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.8 |
| Power BI Report Server | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.7 |
| Azure-related software | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9.3 |
| Microsoft Visual Studio-related software | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.8 |
| Windows Admin Center | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.3 |
| HEVC Video Extensions | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.8 |
| RCE = Remote Code Execution | EOP = Elevation of Privilege | ID = Information Disclosure | SFB = Security Feature Bypass | DOS = Denial of Service | SPF = Spoofing | TMP = Tampering |
Notes:
- Vulnerabilities that overlap components may be represented more than once in the table.
- The summary above is an overview of updates for commonly used software. Updates for older versions, apps, and open source software may not be listed.
- Updates may have been added or removed from the release after this content was finalized.
- Find details for all updates in the monthly release in the Security Update Guide: https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide
- For additional details, see the release notes at: https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/releaseNote/2021-Mar
Resources for deploying updates to remote devices
With so many people working remotely, it is a good time to review guidance on deploying security updates to remote devices, such as desktops, laptops, and tablets. Here are some resources to answer questions pertaining to deploying updates to remote devices.
Part 1: Helping businesses rapidly set up to work securely from personal PCs and mobiles
Part 2: Helping IT send and provision business PCs at home to work securely during COVID-19
Part 3: Manage work devices at home during Covid-19 using Configuration Manager
Part 4: Managing remote machines with cloud management gateway (CMG)
Part 5: Managing Patch Tuesday with Configuration Manager in a remote work world
See also:
Mastering Configuration Manager Bandwidth limitations for VPN connected Clients
Vulnerability details for the current month
Below are summaries for some of the security vulnerabilities in this release. These specific vulnerabilities were selected from the larger set of vulnerabilities in the release for one or more of the following reasons: 1) We received inquiries regarding the vulnerability; 2) the vulnerability may have received attention in the trade press; or 3) the vulnerability is potentially more impactful than others in the release. Because we do not provide summaries for every vulnerability in the release, you should review the content in the Security Update Guide for information not provided in these summaries.
Notes on details in the vulnerability summaries:
| Attack Vector | This metric reflects the context by which vulnerability exploitation is possible. The Base Score increases the more remote (logically, and physically) an attacker can be in order to exploit the vulnerable component. |
| Attack Complexity | This metric describes the conditions beyond the attacker’s control that must exist in order to exploit the vulnerability. Such conditions may require the collection of more information about the target or computational exceptions. The assessment of this metric excludes any requirements for user interaction in order to exploit the vulnerability. If a specific configuration is required for an attack to succeed, the Base metrics should be scored assuming the vulnerable component is in that configuration. |
| Privileges Required | This metric describes the level of privileges an attacker must possess before successfully exploiting the vulnerability. |
| User Interaction | This metric captures the requirement for a user, other than the attacker, to participate in the successful compromise the vulnerable component. This metric determines whether the vulnerability can be exploited solely at the will of the attacker, or whether a separate user (or user-initiated process) must participate in some manner. |
| CVE-2021-24089 | HEVC Video Extensions Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | ||
| Impact | Remote Code Execution | ||
| Severity | Critical | ||
| Publicly Disclosed? | No | ||
| Known Exploits? | No | ||
| Exploitability | Exploitation less likely | ||
| CVSS Score Metrics | Base CVSS Score: 7.8 | Privileges Required: None | Confidentiality: High |
| Attack Vector: Local | User Interaction: Required | Integrity: High | |
| Attack Complexity: Low | Scope: Unchanged | Availability: High | |
| Affected Software: | HEVC Video Extensions | ||
| More Information: | https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability/CVE-2021-24089 |
| CVE-2021-24090 | Windows Error Reporting Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | ||
| Impact | Elevation of Privilege | ||
| Severity | Important | ||
| Publicly Disclosed? | No | ||
| Known Exploits? | No | ||
| Exploitability | Exploitation less likely | ||
| CVSS Score Metrics | Base CVSS Score: 7.8 | Privileges Required: None | Confidentiality: High |
| Attack Vector: Local | User Interaction: Required | Integrity: High | |
| Attack Complexity: Low | Scope: Unchanged | Availability: High | |
| Affected Software: | Windows 10 Version 20H2, Windows 10 Version 2004, Windows 10 Version 1909, Windows Server, version 20H2, Windows Server, version 2004, and Windows Server, version 1909 | ||
| More Information: | https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability/CVE-2021-24090 |
| CVE-2021-26867 | Windows Hyper-V Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | ||
| Impact | Remote Code Execution | ||
| Severity | Critical | ||
| Publicly Disclosed? | No | ||
| Known Exploits? | No | ||
| Exploitability | Exploitation less likely | ||
| CVSS Score Metrics | Base CVSS Score: 9.9 | Privileges Required: Low | Confidentiality: High |
| Attack Vector: Network | User Interaction: None | Integrity: High | |
| Attack Complexity: Low | Scope: Changed | Availability: High | |
| Affected Software: | Windows 10 Version 20H2, Windows 10 Version 2004, Windows 10 Version 1909, Windows Server, version 20H2, Windows Server, version 2004, and Windows Server, version 1909 | ||
| More Information: | https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability/CVE-2021-26867 |
| CVE-2021-27077 | Windows Win32k Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | ||
| Impact | Elevation of Privilege | ||
| Severity | Important | ||
| Publicly Disclosed? | Yes | ||
| Known Exploits? | No | ||
| Exploitability | Exploitation less likely | ||
| CVSS Score Metrics | Base CVSS Score: 7.8 | Privileges Required: Low | Confidentiality: High |
| Attack Vector: Local | User Interaction: None | Integrity: High | |
| Attack Complexity: Low | Scope: Unchanged | Availability: High | |
| Affected Software: | All supported versions of Windows | ||
| More Information: | https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability/CVE-2021-27077 |
| CVE-2021-26897 | Windows DNS Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | ||
| Impact | Remote Code Execution | ||
| Severity | Critical | ||
| Publicly Disclosed? | No | ||
| Known Exploits? | No | ||
| Exploitability | Exploitation more likely | ||
| CVSS Score Metrics | Base CVSS Score: 9.8 | Privileges Required: None | Confidentiality: High |
| Attack Vector: Network | User Interaction: None | Integrity: High | |
| Attack Complexity: Low | Scope: Unchanged | Availability: High | |
| Affected Software: | Windows Server, version 20H2, Windows Server, version 2004, Windows Server, version 1909, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, and Windows Server 2012 | ||
| More Information: | https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability/CVE-2021-26897 |
| CVE-2021-26411 | Internet Explorer Memory Corruption Vulnerability | ||
| Impact | Remote Code Execution | ||
| Severity | Critical | ||
| Publicly Disclosed? | Yes | ||
| Known Exploits? | Yes | ||
| Exploitability | Exploitation detected | ||
| CVSS Score Metrics | Base CVSS Score: 8.8 | Privileges Required: None | Confidentiality: Low |
| Attack Vector: Network | User Interaction: Required | Integrity: High | |
| Attack Complexity: Low | Scope: Changed | Availability: Low | |
| Affected Software: | Internet Explorer 11 on Windows 10 Version 20H2, Windows 10 Version 2004, Windows 10 Version 1909, Windows 10 Version 1809, Windows 10 Version 1803, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, and Windows Server 2012 and Microsoft Edge (EdgeHTML-based) on Windows 10 Version 20H2, Windows 10 Version 2004, Windows 10 Version 1909, Windows 10 Version 1809, Windows 10 Version 1803, Windows Server 2019, and Windows Server 2016 | ||
| More Information: | https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability/CVE-2021-26411 |
| CVE-2021-27076 | Microsoft SharePoint Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | ||
| Impact | Remote Code Execution | ||
| Severity | Important | ||
| Publicly Disclosed? | No | ||
| Known Exploits? | No | ||
| Exploitability | Exploitation more likely | ||
| CVSS Score Metrics | Base CVSS Score: 8.8 | Privileges Required: Low | Confidentiality: High |
| Attack Vector: Network | User Interaction: None | Integrity: High | |
| Attack Complexity: Low | Scope: Unchanged | Availability: High | |
| Affected Software: | Microsoft SharePoint Foundation 2013, Business Productivity Servers 2010, SharePoint Server 2019, and SharePoint Enterprise Server 2016 | ||
| More Information: | https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability/CVE-2021-27076 |
| CVE-2021-27053 | Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | ||
| Impact | Remote Code Execution | ||
| Severity | Important | ||
| Publicly Disclosed? | No | ||
| Known Exploits? | No | ||
| Exploitability | Exploitation less likely | ||
| CVSS Score Metrics | Base CVSS Score: 7.8 | Privileges Required: None | Confidentiality: High |
| Attack Vector: Local | User Interaction: Required | Integrity: High | |
| Attack Complexity: Low | Scope: Unchanged | Availability: High | |
| Affected Software: | Microsoft Office 2019, Office Online Server, 365 Apps for Enterprise, Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2010, and Office Web Apps Server 2013 | ||
| More Information: | https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability/CVE-2021-27053 |